This function implements the Residual (Sur)Realism algorithm as described by Leonard A. Stefanski (2007). It finds a matrix X and vector y such that the fitted values and residuals of lm(y ~ X) are similar to the inputs y_hat and R_0.
Usage
surreal(
data,
y_hat = data[, 1],
R_0 = data[, 2],
R_squared = 0.3,
p = 5,
n_add_points = 40,
max_iter = 100,
tolerance = 0.01,
verbose = FALSE
)Arguments
- data
A data frame or matrix with two columns representing the
y_hatandR_0values.- y_hat
Numeric vector of desired fitted values (only used if
datais not provided).- R_0
Numeric vector of desired residuals (only used if
datais not provided).- R_squared
Numeric. Desired R-squared value. Default is 0.3.
- p
Integer. Desired number of columns for matrix X. Default is 5.
- n_add_points
Integer. Number of points to add in border transformation. Default is 40.
- max_iter
Integer. Maximum number of iterations for convergence. Default is 100.
- tolerance
Numeric. Criteria for detecting convergence and stopping optimization early. Default is 0.01.
- verbose
Logical. If TRUE, prints progress information. Default is FALSE.
References
Stefanski, L. A. (2007). Residual (Sur)Realism. The American Statistician, 61(2), 163-177.
Examples
# Generate a 2D data set
data <- cbind(y_hat = rnorm(100), R_0 = rnorm(100))
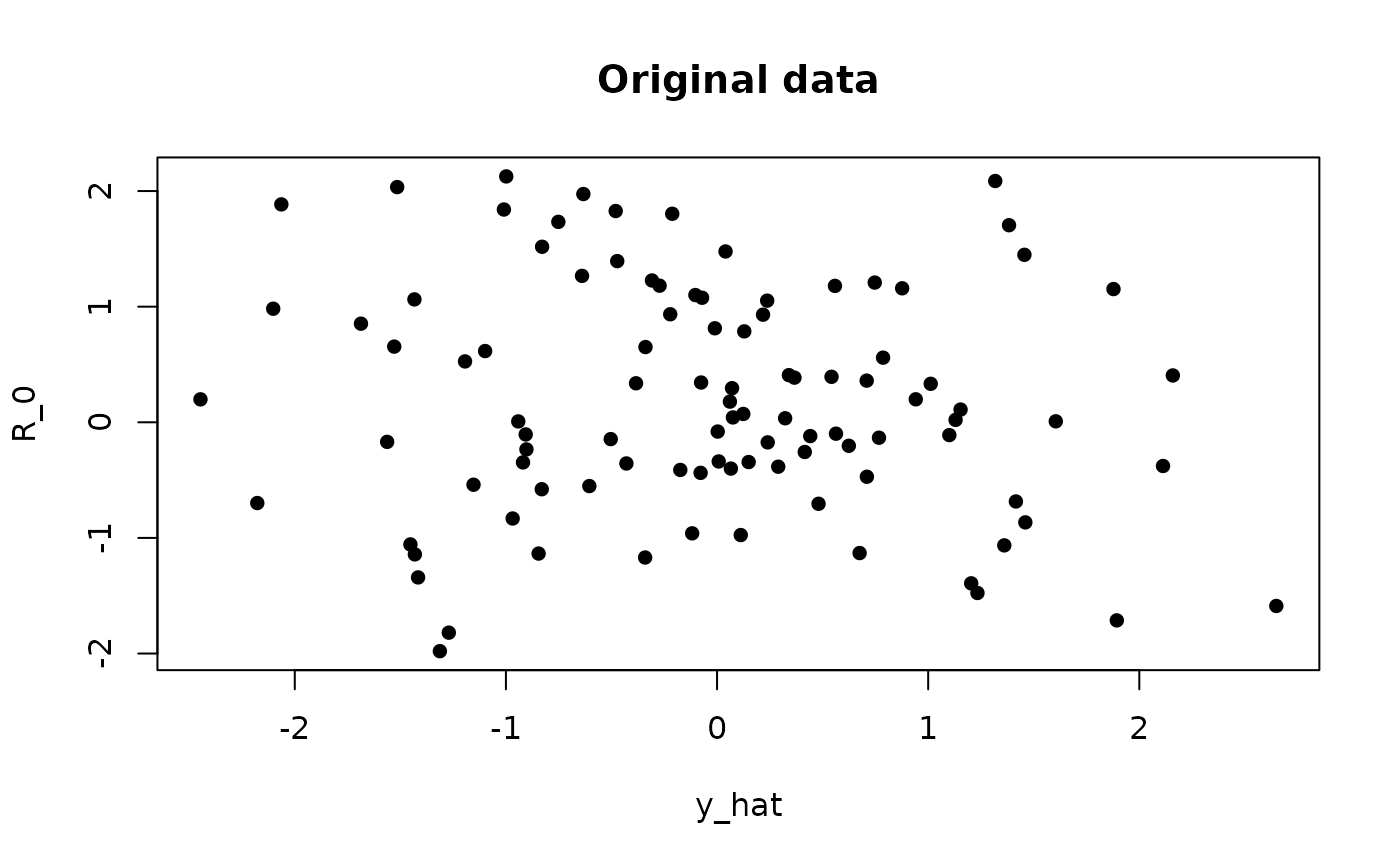
# Display original data
plot(data, pch = 16, main = "Original data")
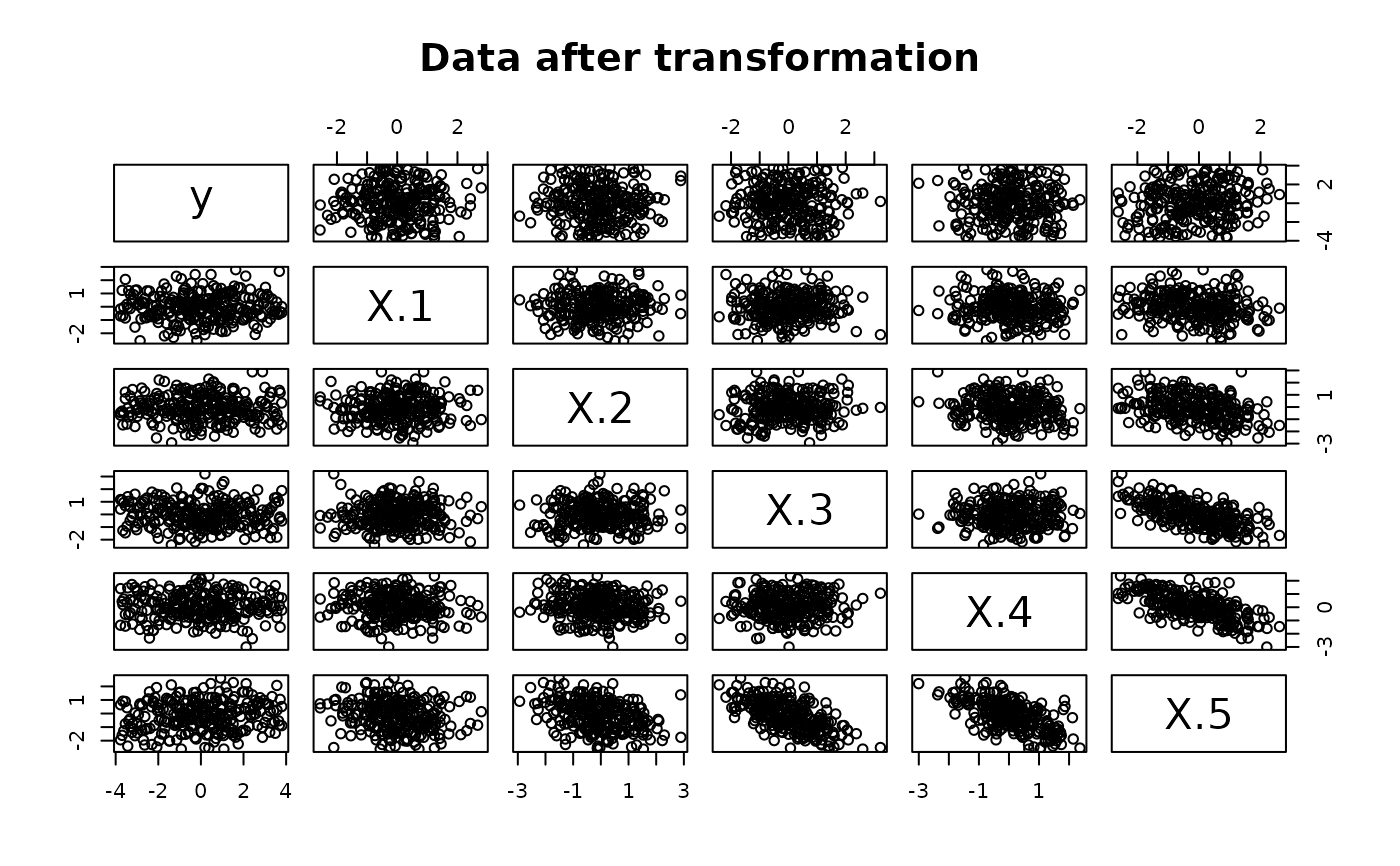
 # Apply the surreal method
result <- surreal(data)
# View the expanded data after transformation
pairs(y ~ ., data = result, main = "Data after transformation")
# Apply the surreal method
result <- surreal(data)
# View the expanded data after transformation
pairs(y ~ ., data = result, main = "Data after transformation")
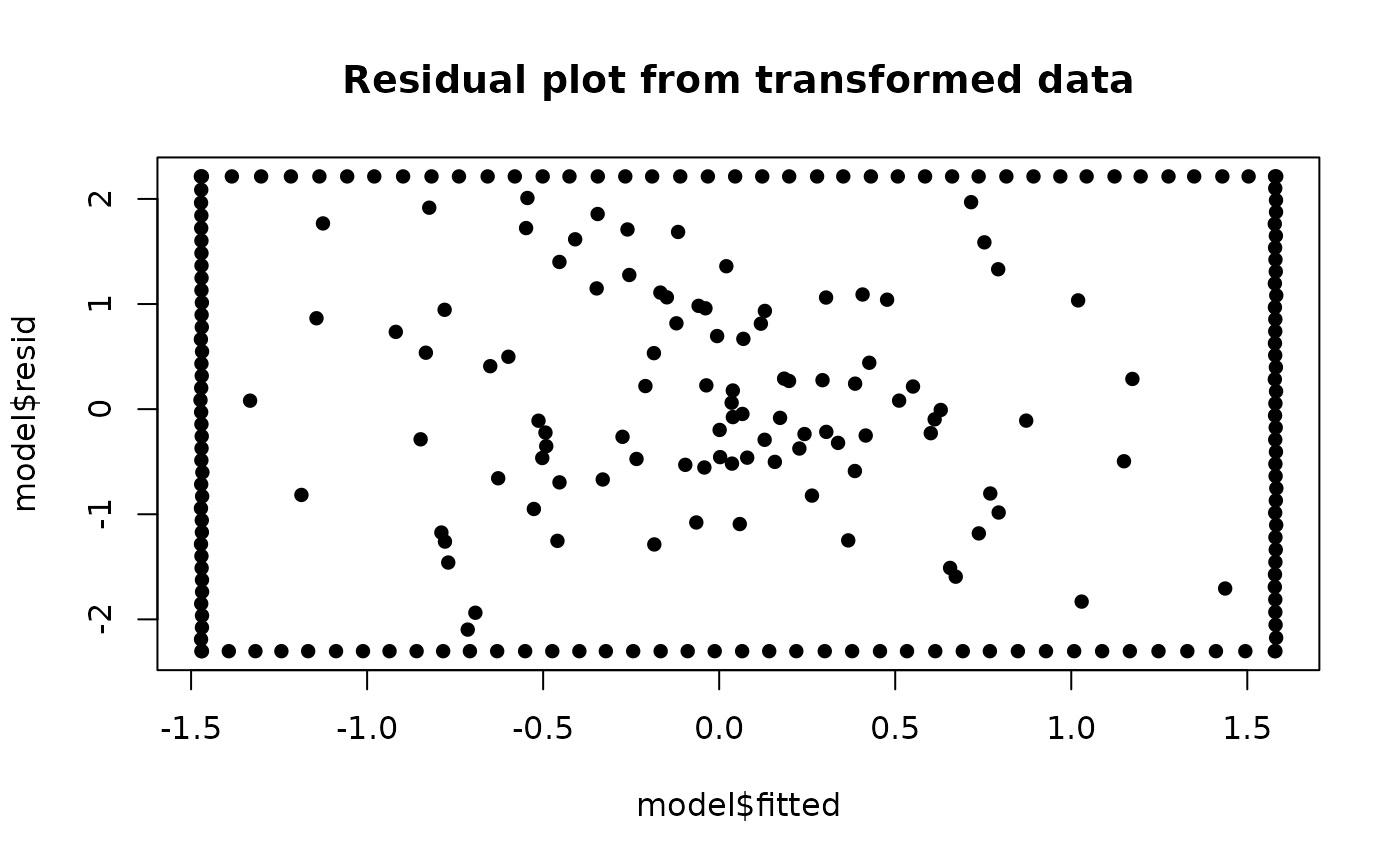
 # Fit a linear model to the transformed data
model <- lm(y ~ ., data = result)
# Plot the residuals
plot(model$fitted, model$resid, type = "n", main = "Residual plot from transformed data")
points(model$fitted, model$resid, pch = 16)
# Fit a linear model to the transformed data
model <- lm(y ~ ., data = result)
# Plot the residuals
plot(model$fitted, model$resid, type = "n", main = "Residual plot from transformed data")
points(model$fitted, model$resid, pch = 16)