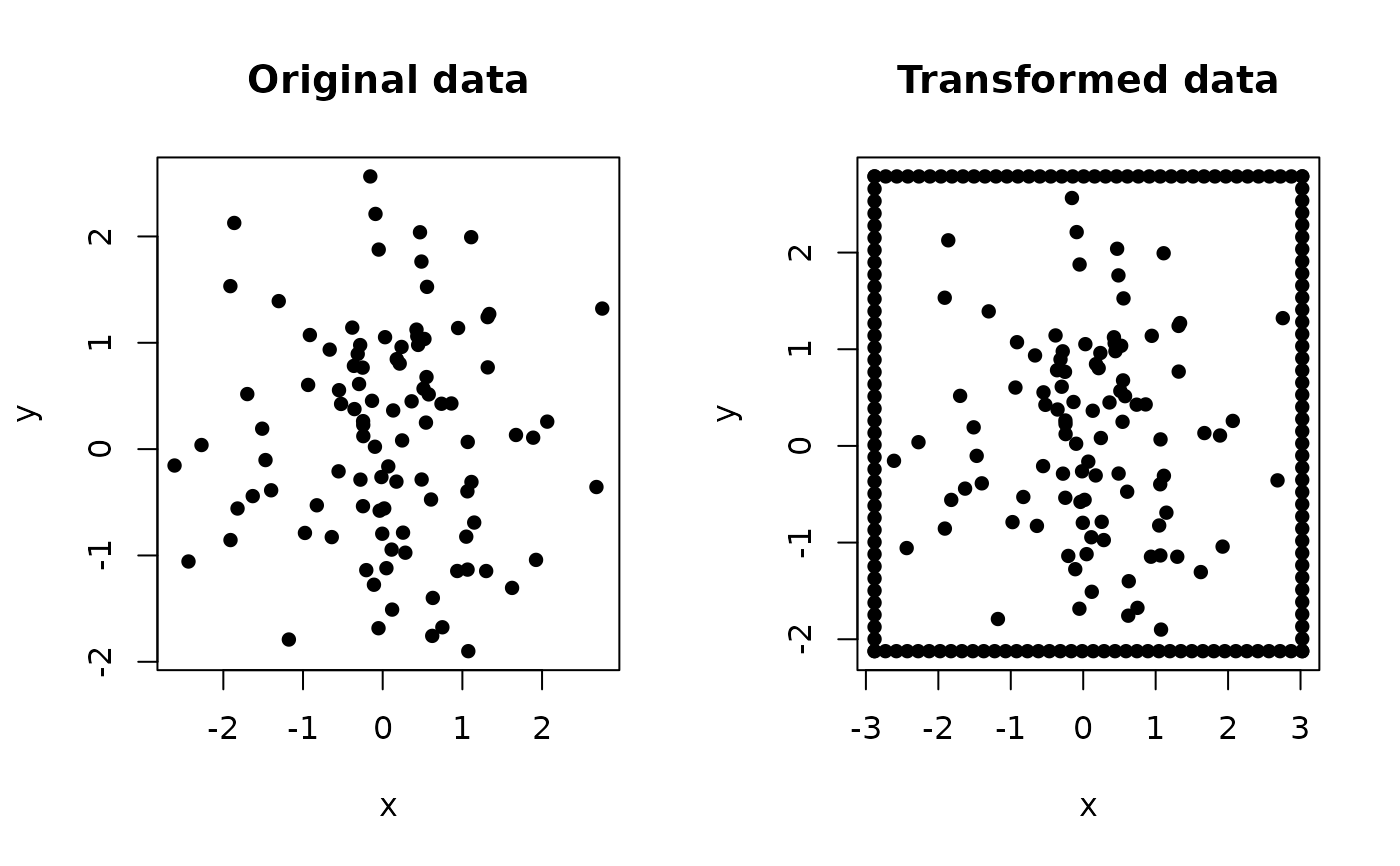
This function transforms the input data by adding points around the original data to create a frame. It uses an optimization process to find the best alpha parameter for point distribution, which helps in making the fitted values and residuals orthogonal.
Examples
# Simulate data
x <- rnorm(100)
y <- rnorm(100)
# Append border to data
transformed_data <- border_augmentation(x, y)
# Modify par settings for plotting side-by-side
oldpar <- par(mfrow = c(1, 2))
# Graph original and transformed data
plot(x, y, pch = 16, main = "Original data")
plot(
transformed_data[, 1], transformed_data[, 2], pch = 16,
main = "Transformed data", xlab = 'x', ylab = 'y'
)
 # Restore original par settings
par(oldpar)
# Restore original par settings
par(oldpar)